Products
APOBEC3G antibody
Category:
Research Area:
| Synonyms: | APOBEC related protein antibody, APOBEC related protein 9 antibody, APOBEC3G antibody, ARCD antibody, ARP 9 antibody, ARP9 antibody, bK150C2.7 antibody, CEM 15 antibody, CEM15 antibody, MDS019 antibody | ||
| Catalogue No.: | FNab00495 | Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Host: | Rabbit | Tested Application: | ELISA, WB, IHC, IF |
| Clonality: | polyclonal | Isotype: | IgG |
- SPECIFICATIONS
- Product Name
- APOBEC3G antibody
- Catalogue No.
- FNab00495
- Size
- 100μg
- Form
- liquid
- Purification
- Immunogen affinity purified
- Purity
- ≥95% as determined by SDS-PAGE
- Clonality
- polyclonal
- Isotype
- IgG
- Storage
- PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3, -20℃ for 12 months(Avoid repeated freeze / thaw cycles.)
Immunogen
- Immunogen
- apolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme, catalytic polypeptide-like 3G
- Alternative Names
- APOBEC related protein antibody, APOBEC related protein 9 antibody, APOBEC3G antibody, ARCD antibody, ARP 9 antibody, ARP9 antibody, bK150C2.7 antibody, CEM 15 antibody, CEM15 antibody, MDS019 antibody
- UniProt ID
- Q9HC16
- Observed MW
- 46 kDa
Application
- Tested Applications
- ELISA, WB, IHC, IF
- Recommended dilution
- WB: 1:200-1:1000; IHC: 1:20-1:200; IF: 1:20-1:200
Validated Images
 mouse colon tissue were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with FNab00495(APOBEC3G Antibody) at dilution of 1:100
mouse colon tissue were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with FNab00495(APOBEC3G Antibody) at dilution of 1:100
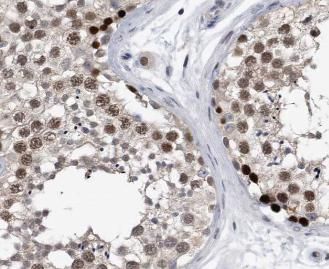 Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human testis tissue slide using FNab00495(APOBEC3G Antibody) at dilution of 1:200
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human testis tissue slide using FNab00495(APOBEC3G Antibody) at dilution of 1:200
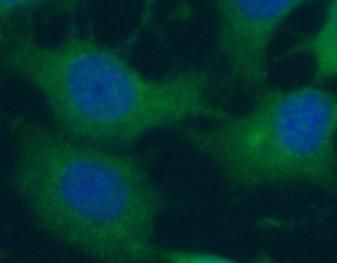 Immunofluorescent analysis of MCF-7 cells using FNab00495 (APOBEC3G antibody) at dilution of 1:50 and Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L)
Immunofluorescent analysis of MCF-7 cells using FNab00495 (APOBEC3G antibody) at dilution of 1:50 and Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L)
- Background
- DNA deaminase(cytidine deaminase) which acts as an inhibitor of retrovirus replication and retrotransposon mobility via deaminase-dependent and-independent mechanisms. Exhibits potent antiviral activity against vif-deficient HIV-1. After the penetration of retroviral nucleocapsids into target cells of infection and the initiation of reverse transcription, it can induce the conversion of cytosine to uracil in the minus-sense single-strand viral DNA, leading to G-to-A hypermutations in the subsequent plus-strand viral DNA. The resultant detrimental levels of mutations in the proviral genome, along with a deamination-independent mechanism that works prior to the proviral integration, together exert efficient antiretroviral effects in infected target cells. Selectively targets single-stranded DNA and does not deaminate double-stranded DNA or single-or double-stranded RNA. Exhibits antiviral activity also against simian immunodeficiency viruses(SIVs), hepatitis B virus(HBV), equine infectious anemia virus(EIAV), xenotropic MuLV-related virus(XMRV) and simian foamy virus(SFV). May inhibit the mobility of LTR and non-LTR retrotransposons.



